- SITEMAP
- CONTACT US
- 8618267732328
News
Credibility ,the lifeblood of enterprise!
- Fittings
- Butt Welding Fittings
- Forged Fittings
- 180 Degree Elbows
- 90 Degree Elbows
- 60 Degree Elbows
- 45 Degree Elbows
- 30 Degree Elbows
- Equal Tee
- Reducing Tee
- Concentric Reducer
- Eccentric Reducer
- Lap Joint Stub End
- Outlets
- Cap
- Bend
- Cross
- Coupling
- Stainless Steel Lateral Tee
- Bellows Expansion Joints
- Flexible Metal Hose
- Non-Standard/Custom Fittings
- Bleed & Flushing Rings
- Types of Flanges
- Anchor Flanges
- Blind Flanges
- Expander Flanges
- High Hub Flanges
- Lap Joint Flanges
- Long Weld Neck Flanges
- Nipoflanges
- Orifice Flanges
- Plate Flanges
- Ring Type Joint Flanges
- Reducing Flanges
- Slip On Flanges
- Socket Weld Flanges
- Spectacle Blind Flanges
- Square Flanges
- Spades & Ring Spacers
- Threaded Flanges
- Welding Neck Flanges
Pitting of steel
What is pitting corrosion?
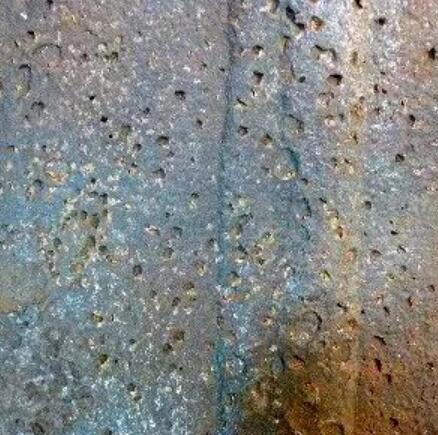

Pitting mechanism of steel
Steel surface passivation film due to the presence of defects in the steel, inclusions and solute inhomogeneity, so that the passivation film in these places more fragile, in a specific corrosive solution is easy to be destroyed, the damaged part will become activated anode, the surrounding area becomes the cathode area, the area ratio of the two is very small, the current density of the anode is very large, the active dissolution is accelerated, then become many needle-like pores.

1. Etching hole formation stage
MnS+4H2O=Mn2++SO42-+8H++8e
2. The expansion of the long corrosion source and the development stage of pitting corrosion
Men++nH2O=Me(OH)n+nH+
The pH of the solution layer in contact with the small etch pits decreases, forming a strong hard solution zone, which in turn accelerates the dissolution of the metal and makes the etch holes widen and deepen. With the deepening of the corrosion hole and the formation of corrosion products covering the pit, so that the hole inside and outside the solution between the material migration more solid difficult, the hole metal salts more and more concentrated. This on the one hand by the decomposition of its water leading to a growing decline in pH; on the other hand, by the excess of positive charge in the hole to form an electric field, so that Cl- through the pore and corrosion products (cover) pores through electrophoresis constantly diffuse in, resulting in the enrichment of Cl- in the hole. This with the local corrosion process, so that the occlusion area (within the etch) more and more acidification process is called "autocatalytic acidification process". The pH of the solution in the etched hole and Cl- enrichment can reach a very serious degree. This strong acid environment in the etched hole makes the inner wall of the etched hole in the active state, as the anode; while a large area of the metal surface outside the hole is still in the blunt state, as the cathode, constituting an active state - blunt state battery system composed of small anode sub-cathode, so that the etched hole accelerates the expansion and deepening. The potential of this battery (the potential difference between the inner and outer surface of the etched hole) is the driving force for the development of pitting corrosion. The reaction inside the hole etching can be summarized in the following figure.
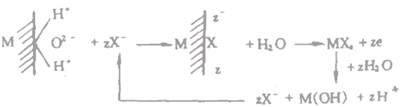
Reaction inside the pitting

Tel No:+86-18267732328 / Email:[email protected]
Address:Longwan District, Wenzhou, Zhejiang Province, China.
Copyright Notice © www.yaang.com Yaang Pipe Industry Co., Limited All rights reserved.
Yaang Pipe Industry Co., Ltd. is an international supplier of piping solutions for flange, butt welding fittings, socket welding fittings and threaded fittings. Our products are widely used in different industrial fields, including oil and gas, chemical industry, petrochemical industry, power plant, pulp and paper industry, environmental and water conservancy engineering, engineering projects, etc.





